AI in German Manufacturing
Market, applications & international comparison
Germany is currently in a dynamic phase of implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) in industrial production. The growth rates are remarkable: the German AI market is expected to increase from €4.8 billion in 2022 to around €10 billion by 2025 – an annual growth rate of approximately 30 percent. Long-term projections are even more ambitious, forecasting a market volume of roughly €32.16 billion by 2030.
Despite these positive trends, there are differences in the intensity of adoption. According to a study by the German Economic Institute (IW Koeln), 37 percent of German companies are already using AI technologies, although often only selectively and with a focus on free tools. In the manufacturing sector specifically, the figures are more encouraging: over 40 percent of industrial companies are already actively integrating AI into their production processes.

Industry-specific AI Adoption in Germany
The introduction of AI in German industry is progressing at different speeds across sectors. While some industries already have a high level of digitalization and automation, others are still in the early stages but are now catching up quickly. The table below shows the projected spread of AI use by 2025:
Sector/Industry
AI Adoption Rate
Comment
Overall Industry
> 40 %
A significant share of industrial companies already use one or more AI solutions – often in quality control, predictive maintenance, or process optimization. AI is increasingly becoming a standard tool in production.
Mass Production
21 % active use
An additional 11 % of companies plan to implement AI by the end of 2025. The focus here is on increasing efficiency and throughput through automated production lines and AI-controlled assembly processes.
Electrical Industry
19 % new adopters
High growth potential, as many companies have used little AI so far. The expected increase is driven by rising demand for smart production processes, robotics, and digital quality control.
Mechanical Engineering
10 % new adopters
Although traditionally an innovation driver, AI use is often project-based. The trend is now moving towards smart machine control systems, digital twins, and AI-supported service offerings.
Key Areas of Application
The main areas of AI adoption in Germany can be grouped into five core categories:
- Robotics & Automation: Intelligent robotic systems that can adapt to different product variants and perform highly precise assembly work.
- Quality Control & Defect Detection: Deep learning models for automated inspections that reduce failure rates and cut production costs.
- Digital Twins & Simulation: Virtual replicas of production facilities to optimize planning and reduce risks.
- Predictive Maintenance: Real-time machine data analysis to predict maintenance needs early and avoid unplanned downtime.
- Process Optimization: Use of generative AI to automatically create part designs and production programs directly from CAD data.
Germany vs. China (vs. USA)
An international comparison reveals significant differences in the speed of implementation and strategic focus:
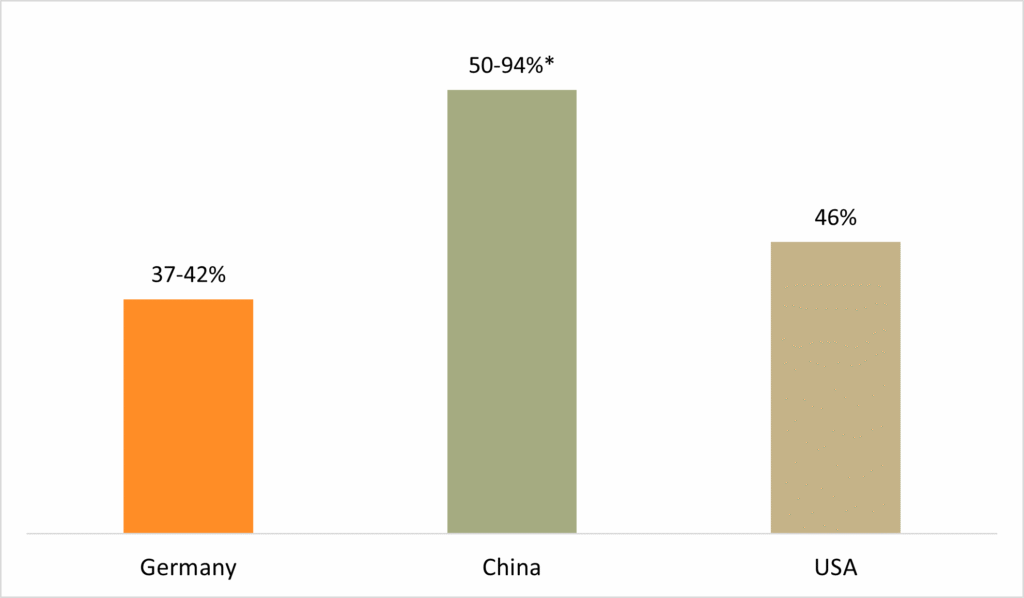
Share of companies using AI in production
Strategic focus and implementation approach
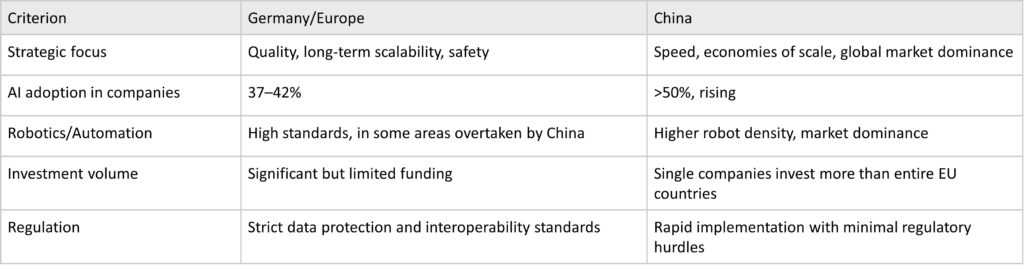
Germany/Europe and China follow markedly different strategies in AI-driven manufacturing. Germany focuses on quality, long-term scalability, and safety, while China emphasizes speed, large-scale deployment, and global market dominance.
AI usage in Germany stands at 37–42 percent, while in China it is already over 50 percent and continues to rise. Higher robot densities, enormous investments by individual companies, and a largely unregulated framework give China speed and market advantages, while Germany builds on stability and trust through strict standards.
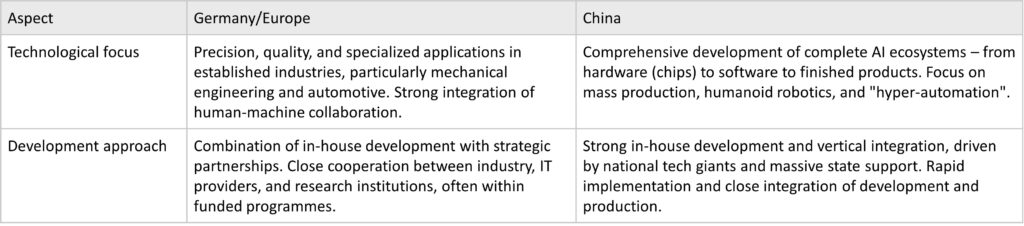
Technological Focus and Development Approaches Compared
The technological priorities and development strategies of Germany/Europe and China differ fundamentally – both in the nature of applications and in how research and production are organised.
Investment Comparison
A look at global investments in AI for manufacturing reveals substantial differences in financial firepower, with China leading, followed by the USA and, far behind, Germany:
AI investments in production worldwide in billion USD

Best Practice Examples
Case studies from leading industrial companies illustrate how differently Germany and China are deploying AI in manufacturing – and how each approach reflects its strengths. German companies tend to focus on precise, quality-oriented solutions in complex production environments, while Chinese companies are striving for rapid, comprehensive, and highly scalable integration.
Germany
- BMW Group – AIQX Initiative: Revolutionizes quality assurance through AI, connecting production processes via Car2X technology.
- Siemens – Industrial Copilot & MTR: CNC robots with adaptive control, AI-driven process automation, and predictive maintenance.
- Bosch: Deep learning models for automated defect detection.
- TRUMPF: Neural networks for automatic sheet metal sorting.
- Festo: Standardized AI app for cylinder monitoring in pneumatic systems.
China
- Estun Automation: Industrial robots with real-time AI optimization.
- CRRC: Autonomous system tests and process monitoring in locomotive production.
- SMEE: AI-based quality control in semiconductor manufacturing.
- Foxconn China: Large-scale integration of AI robotics in electronics manufacturing.
Conclusion
Germany is in a transitional phase of industrial AI transformation. With an adoption rate of 37–42 percent, the country ranks solidly in the global middle but lags far behind China in implementation speed. The next few years will be decisive in determining whether Germany can drive large-scale AI integration in manufacturing or whether China’s lead will continue to grow.
Germany’s strengths are its focus on quality and the complex integration of AI into high-end production, particularly in mechanical engineering and automotive. It benefits from a strong research landscape, including institutions such as the Fraunhofer Institutes and leading universities, and from the innovative strength of its medium-sized companies, which deliver specialized, practice-oriented solutions. A stable regulatory framework also builds trust among companies and investors.
In contrast, China’s dynamism is driven by an overwhelming investment volume that far exceeds Germany’s, massive state-led funding, and rapid, large-scale implementation through vertical integration. With its vision of full automation by 2040, China is pursuing a long-term but highly ambitious strategy to secure global leadership in industrial AI applications.
Silke Hänisch, Market Intelligence Senior Expert
Sources:
- Bitkom Research: KI-Adoption in der deutschen Industrie, 15.04.2025
- IW Köln: KI als Wettbewerbsfaktor für die deutsche Industrie, 28.02.2025
- VDMA: Künstliche Intelligenz in der Produktion, 20.09.2024
- Siemens, Bosch, BMW, TRUMPF – Unternehmensangaben, Q1/2025
- table.media: Chinas KI-Entwicklung, 18.02.2025
- evertiq.de: KI-Investitionen in China, 21.01.2025
- GTAI: China AI Industry Report, 09.03.2025






